Authors
Tessa Minter & Carlos Correia
Abstract
The key to maximising the effectiveness of spreadsheet models for critical decision making is appropriate risk governance. Those responsible for governance need, at a macro level, to identify the specific spreadsheet risks, determine the reasons for such exposures and establish where and when risk exposures occur from point of initiation to usage and storage.
It is essential to identify which parties could create the exposure taking cognisance of the entire supply chain of the organisation. If management's risk strategy is to control the risks then the question reverts to how these risks can be prevented and/or detected and corrected?
This paper attempts to address each of these critical issues and to offer guidance in the governance of spreadsheet risk. The paper identifies the risk exposures and sets out the responsibilities of directors in relation to spreadsheets and the spreadsheet cycle.
Spreadsheet risk exposure can be managed in terms of setting the control environment, undertaking risk assessment, providing the requisite information and communicating with internal and external parties as well as implementing spreadsheet lifecycle application controls and monitoring activities.
Sample
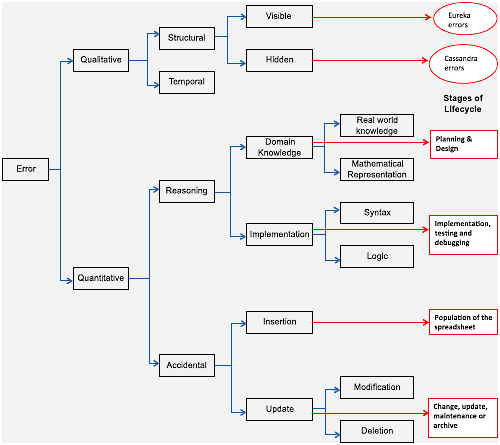
This classification of spreadsheet errors is closely associated with the spreadsheet lifecycle.
Note the qualitative aspect of temporal errors, referring to those using out of date data and the concept of hidden errors which are not visible except in use.
Publication
2014, Risk governance & control: Financial markets & institutions, Volume 4, Issue 2, pages 7-15
Full article
The governance of risk arising from the use of spreadsheets in organisations
