Authors
Rainer Lueg & Lu Shijia
Abstract
Over the past three decades, the reliance on sophisticated spreadsheets for budgeting has emerged as a standard in most organizations (Hesse and Hesse Scerno, 2009). Despite these technological advancements, rich empirical evidence documents that technologically induced 'spreadsheet errors' can substantially lower the accuracy of spreadsheets (Powell et al., 2009). These errors lead to suboptimal decision making and biased performance assessment.
The aim of this paper is to examine how spreadsheet error can be detected and prevented in the budgeting process. The research design applies models of spreadsheet accuracy testing (SAT) from Kruck (2006) and Vessey (1985). The paper,
The authors base the analyses on a unique dataset (interviews, participating observations, technical artifacts) gathered through 'action research' at a Chinese-Danish government organization, which uses budgets for assessing applications on research funding. Our results confirm and extend existing theory in the field of budgeting and SAT and provide interesting findings.
First, the paper shows that later spreadsheet error in budgeting is already rooted in a poor conceptualization of the budget template, in non-workflow-oriented imputation of data and poor documentation of data requirements. Second, it illustrates how the accuracy of spreadsheets substantially improves by introducing even simplistic VBA. Third, we present evidence that the flexibility of the budgeting template itself to changes in the organizational environment fosters spreadsheet accuracy in the long term.
Sample
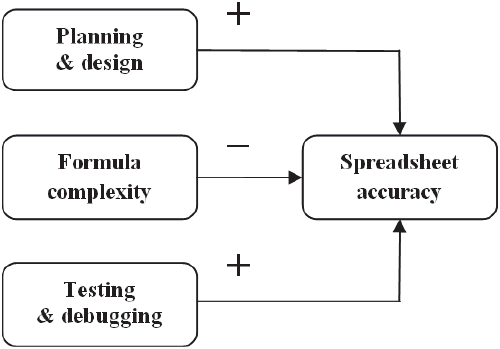
Spreadsheet accuracy improves substantially with the three factors of: careful planning and design, low formula complexity, and extensive testing.
Publication
2012, Problems and Perspectives in Management, Volume 10, Issue 1, pages 32-41
Full article
Improving efficiency in budgeting: An interventionist approach to spreadsheet accuracy testing
