Authors
Sasa Baskarada
Abstract
Spreadsheet applications, and in particular Microsoft Excel, are now ubiquitous. Even though, many large organisations heavily rely on them for data analysis, management reporting, and decision making, limited research regarding their potential impacts on organisational information quality has been published.
This paper aims to bridge that gap in the literature by identifying key factors - inherent to spreadsheet applications as well as related to their use - which may have significant negative effects on information quality in organisations.
The findings presented in this paper have been identified as a part of a broader ethnographic study on information quality, which was conducted in a large telecommunications company over a period of six months.
This paper shows that the diffusion of spreadsheet applications is driven by reporting limitations inherent in existing transactional and Business Intelligence (BI) systems. However, while the use of spreadsheets may often be justified from the operational perspective, it frequently leads to significant negative effects on the quality of relevant information.
Sample
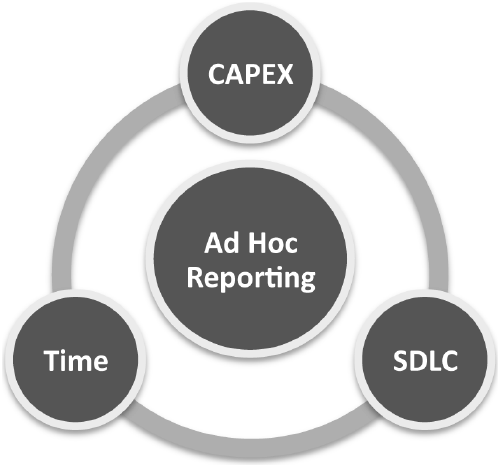
This study has identified ad hoc reporting as the main use of spreadsheet applications. Even though most of the transactional — and certainly all BI — systems provide reporting functionalities, several reasons why they are not commonly used have been identified:
- Lack of capital expenditure (CAPEX) funding.
- The System Development Life Cycle (SDLC) process is too complex.
- The time frame required for development is too long.
Publication
2011, The Journal of Computer Information Systems, Volume 51, Number 3, Spring, pages 77-84
