Authors
Hock Chuan Chan, Suparna Goswami, & Hee Woong Kim
Abstract
This paper uses cognitive fit theory to analyze the problem solving process in spreadsheet analyses. Cognitive fit theory proposes the formation of mental representation as a part of the problem solving process. However, there is little research examining mental representation, which is a key concept in cognitive fit theory.
This study examines the formation of mental representation and proposes an alternative mechanism of cognitive fit between different problem representations and their corresponding mental representations when the task is invariant, but the problem representation changes. Mental representation is then empirically assessed based on the application of Hick's law, which states that the response time of users making a choice varies with the logarithm of the number of possible choices.
Therefore, this study contributes to research on cognitive fit theory by proposing an alternative fit and by demonstrating a feasible approach for identifying mental representations. It contributes to spreadsheet research by showing how problem representations affect task performance in the case of spreadsheet error correction.
Sample
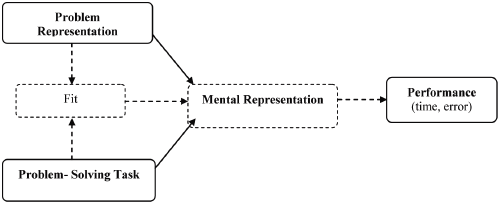
This figure depicts the cognitive fit theory, where fit is explained as a match between the information in the task and the information in the problem representation. The implication of fit is better problem solving performance, mostly measured in terms of time taken to perform the task and the number of errors made.
Publication
2012, Journal of Database Management, Volume 23, Number 2, April-June, pages 22-43
Full article
An alternative fit through problem representation in cognitive fit theory
